코딩/백준-알고리즘
[백준] 5979 남땜하기 C++ (Feat 고찰)
안녕 나의 20대
2024. 5. 28. 17:59
반응형
Li Chao Segment Tree를 사용하여 최소 비용 트리 문제를 해결하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다. 이 알고리즘은 주어진 트리 구조에서 비용을 최소화하는 경로를 찾는 데 사용됩니다. 해당 알고리즘을 C++로 구현합니다
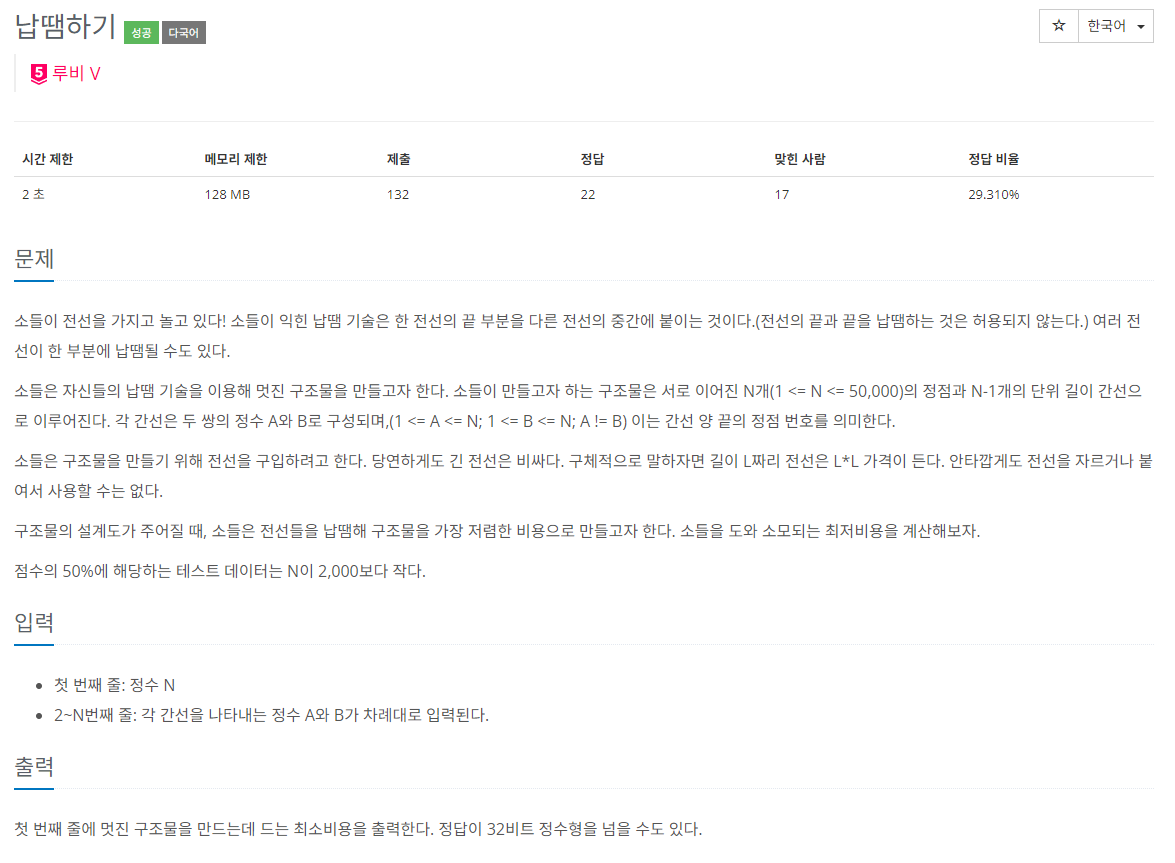
문제 설명
주어진 트리에서 각 노드를 방문하는 비용이 정의되어 있을 때, 특정 노드에서 시작하여 모든 노드를 방문하는 최소 비용을 계산하는 문제입니다. 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 우리는 Li Chao Segment Tree라는 자료 구조를 사용합니다.
Li Chao Segment Tree란?
Li Chao Segment Tree는 선형 함수들의 최소값을 구하는 데 최적화된 자료 구조입니다. 이 자료 구조는 Convex Hull Trick과 비슷하지만, 세그먼트 트리의 형태로 구현되어 특정 범위 내의 선형 함수의 최소값을 구할 수 있습니다.
구현 방법
먼저 C++로 구현된 코드 입니다
C++ 코드
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll inf = 1e18;
// 라인 구조체 정의
struct Line {
ll a, b;
ll f(ll x) { return a * x + b; }
};
// Li Chao Segment Tree 구조체 정의
struct Lichao {
struct Node {
ll l, r;
Line line;
};
ll n, psum, ns, ne;
vector<Node> seg;
vector<Line> lines;
// 초기화 함수
void init(int s, int e) {
ns = s, ne = e;
seg.push_back({ -1, -1, {0, inf} });
}
// 라인 개수를 반환하는 함수
int size() { return lines.size(); }
// 라인을 삽입하는 함수
void insert(int num, int s, int e, Line l) {
Line lo = seg[num].line, hi = l;
if (lo.f(s) > hi.f(s)) swap(lo, hi);
if (lo.f(e) <= hi.f(e)) {
seg[num].line = lo;
return;
}
int mid = (s + e) >> 1;
if (lo.f(mid) < hi.f(mid)) {
seg[num].line = lo;
if (seg[num].r == -1) {
seg[num].r = seg.size();
seg.push_back({ -1, -1, {0, inf} });
}
insert(seg[num].r, mid + 1, e, hi);
} else {
seg[num].line = hi;
if (seg[num].l == -1) {
seg[num].l = seg.size();
seg.push_back({ -1, -1, {0, inf} });
}
insert(seg[num].l, s, mid, lo);
}
}
// 라인을 삽입하는 함수
void insert(Line l) {
l.b -= psum;
lines.push_back(l);
insert(0, ns, ne, l);
}
// 모든 라인에 psum을 적용하는 함수
void apply() {
for (auto& l : lines) l.b += psum;
for (auto& seg_node : seg) seg_node.line.b += psum;
psum = 0;
}
// 주어진 x에 대해 최소값을 찾는 함수
ll query(int num, int s, int e, ll x) {
if (num == -1) return inf;
int mid = (s + e) >> 1;
ll d = seg[num].line.f(x) + psum;
if (x <= mid) return min(d, query(seg[num].l, s, mid, x));
else return min(d, query(seg[num].r, mid + 1, e, x));
}
// 외부에서 호출 가능한 query 함수
ll query(ll x) { return query(0, ns, ne, x); }
};
// 상수 및 전역 변수 정의
const ll MAX = 50001;
vector<ll> V[MAX], G[MAX], dp[MAX], vec[MAX];
ll n, par[MAX], ind[MAX], dep[MAX];
Lichao li[MAX];
// 깊이 우선 탐색 함수
void dfs(int pos, int d = 0, int p = 0) {
par[pos] = p;
dep[pos] = d;
for (ll w : V[pos]) {
if (w == p) continue;
G[pos].push_back(w);
dfs(w, d + 1, pos);
}
}
// 제곱 계산 함수
ll pw(ll x) { return x * x; }
// DP를 채우는 함수
void fillDP(int pos) {
ll sum = 0;
for (auto& w : G[pos]) {
ll d = li[w].query(dep[pos]) + pw(dep[pos]);
sum += d;
vec[pos].push_back(d);
}
dp[pos][0] = sum;
for (int i = 1; i <= G[pos].size(); i++)
dp[pos][i] = sum - vec[pos][i - 1];
}
// Li Chao Segment Tree 병합 함수
void merge(int pos) {
ll sum = dp[pos][0];
ll x = dep[pos];
vector<Line> newLines;
for (int i = 0; i < G[pos].size(); i++) {
ll w = G[pos][i];
if (li[w].size() <= li[pos].size()) {
li[w].apply();
for (auto& l : li[w].lines) {
ll l1 = l.f(2 * x), c = -sum + dp[pos][i + 1] + 4 * pw(x);
ll y1 = -l.a / 2;
newLines.push_back({ -2 * x, li[pos].query(2 * x - y1) + l1 + c + pw(x) });
}
for (auto& l : li[w].lines) {
l.b += dp[pos][i + 1];
li[pos].insert(l);
}
} else {
li[w].psum += dp[pos][i + 1];
li[pos].apply();
for (auto& l : li[pos].lines) {
ll l1 = l.f(2 * x), c = -sum + 4 * pw(x);
ll y1 = -l.a / 2;
newLines.push_back({ -2 * x, li[w].query(2 * x - y1) + l1 + c + pw(x) });
}
for (auto& l : li[pos].lines)
li[w].insert(l);
swap(li[w], li[pos]);
}
}
for (auto& l : newLines) li[pos].insert(l);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
// 그래프 입력
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u, v; cin >> u >> v;
V[u].push_back(v);
V[v].push_back(u);
}
// 루트 노드 선택
int root = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (V[i].size() == 1) {
root = i;
break;
}
}
// DFS 실행
dfs(root);
// DP 및 Li Chao Segment Tree 초기화
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ind[i] = G[i].size();
dp[i].resize(ind[i] + 1, inf);
li[i].init(0, n);
}
// BFS를 위한 큐 초기화
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!ind[i]) {
q.push(i);
dp[i][0] = 0;
li[i].insert({ -2 * dep[i], pw(dep[i]) });
}
}
// BFS 실행 및 DP 병합
while (!q.empty()) {
int top = q.front(); q.pop();
int t = par[top];
if (--ind[t] == 0) {
q.push(t);
fillDP(t);
merge(t);
}
}
// 결과 출력
cout << dp[root][0];
return 0;
}코드 설명
- 데이터 구조 정의:
- Line 클래스: 선형 함수를 정의합니다.
- Node 클래스: Li Chao Segment Tree의 노드를 정의합니다.
- Lichao 클래스: Li Chao Segment Tree를 구현합니다.
- 입력 및 초기화:
- 트리의 노드와 간선을 입력받아 초기화합니다.
- 깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS):
- 반복문을 사용하여 재귀 깊이 제한 문제를 해결합니다.
- 동적 계획법 (DP) 채우기:
- 각 노드의 DP 값을 계산합니다.
- Li Chao Segment Tree 병합:
- 노드의 DP 값을 Li Chao Segment Tree에 병합합니다.
- 결과 출력:
- 계산된 최소 비용을 출력합니다.
번외
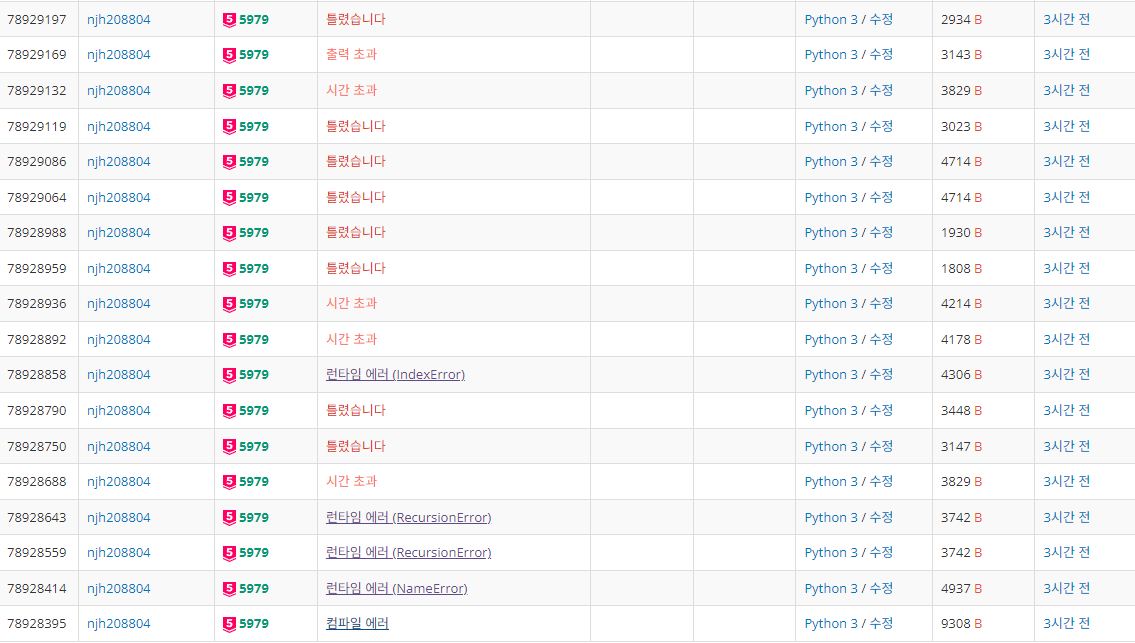
파이썬으로도 해결해보려 노력했지만 많은 실패가 있었다
파이썬으로 성공하신분이 있다면 조언 부탁드립니다 :)
아래는 시간초과로 실패했던 파이썬 코드입니다
import sys
import math
from collections import defaultdict
# Increase the recursion limit to handle deep recursions
sys.setrecursionlimit(10**6)
inf = 1e11
class Line:
def __init__(self, x=0, y=inf):
self.x = x
self.y = y
def f(self, x):
return self.x * x + self.y
def __lt__(self, other):
return self.x < other.x if self.x != other.x else self.y < other.y
class ConvexHullTrick:
def __init__(self):
self.joo = []
self.boo = []
def size(self):
return len(self.joo) + len(self.boo)
def bad(self, a, b, c):
return (a.y - b.y) * (c.x - b.x) <= (b.y - c.y) * (b.x - a.x)
def renew(self):
aux = sorted(self.boo + self.joo)
self.joo = []
self.boo = []
for i in aux:
if self.joo and self.joo[-1].x == i.x:
continue
while len(self.joo) >= 2 and self.bad(self.joo[-2], self.joo[-1], i):
self.joo.pop()
self.joo.append(i)
def add(self, l):
if len(self.boo) >= 200:
self.renew()
self.boo.append(l)
def query(self, x):
ret = inf
for l in self.boo:
ret = min(ret, l.f(x))
if self.joo:
s, e = 0, len(self.joo) - 1
while s != e:
m = (s + e) // 2
if self.joo[m].f(x) < self.joo[m + 1].f(x):
e = m
else:
s = m + 1
ret = min(ret, self.joo[s].f(x))
return ret
def retrieve(self):
return self.joo + self.boo
class DP:
def __init__(self):
self.cht = ConvexHullTrick()
self.offsetx = 0
self.offsety = 0
self.offsetq = 0
def size(self):
return self.cht.size()
def add(self, l):
l.x -= self.offsetx
l.y -= self.offsety
l.y -= self.offsetq * l.x
self.cht.add(l)
def shift_line(self, x, y):
self.offsetx += x
self.offsety += y
def change_query(self, x, y):
self.offsety += y + self.offsetx * x
self.offsetq += x
def query(self, x):
return self.cht.query(x + self.offsetq) + self.offsetx * x + self.offsety
def retrieve(self):
ret = self.cht.retrieve()
for i in ret:
i.y += self.offsety + self.offsetq * i.x
i.x += self.offsetx
return ret
def solve(x):
if not gph[x]:
ret = DP()
ret.add(Line(1, 0))
opt[x] = 1
return ret
sumv = 0
minv = inf
cur = DP()
for i in gph[x]:
tmp = solve(i)
if cur.size() < tmp.size():
cur, tmp = tmp, cur
tv = tmp.retrieve()
for j in tv:
minv = min(minv, cur.query(2 * j.x) + j.y + 1)
for j in tv:
cur.add(j)
sumv += opt[i]
cur.shift_line(1, sumv)
cur.change_query(2, -1)
cur.add(Line(1, minv + sumv))
global ans
ans = minv + sumv - 1
opt[x] = cur.query(0)
cur.shift_line(0, -opt[x])
return cur
def dfs(x):
for i in gph[x]:
gph[i].remove(x)
dfs(i)
if __name__ == "__main__":
input = sys.stdin.read
data = input().split()
n = int(data[0])
if n == 1:
print(0)
sys.exit(0)
if n == 2:
print(1)
sys.exit(0)
gph = defaultdict(list)
index = 1
for _ in range(n - 1):
s = int(data[index])
e = int(data[index + 1])
index += 2
gph[s].append(e)
gph[e].append(s)
root = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
if len(gph[i]) > 1:
root = i
break
opt = [0] * (n + 1)
ans = inf
dfs(root)
solve(root)
print(ans)반응형